Chromatography
in a few words
Chromatography is a technique for separating molecules in a liquid mixture using a stationary phase, here resin beads.
The molecules will be separated according to their difference of affinity with the resin resulting on a difference of speed through the system. Because it’s based on affinity difference, it aims to separate compounds without regenerant use (means without chemicals classically used for regeneration). This technology is commonly used at laboratory scale for analyses but also at industrial scale for food, pharma and biotech industries.
At Applexion, we mainly apply chromatography using water as an eluent. It is therefore the perfect green process of purification without the use of chemicals, nor effluents.
Chromatography
Industrial technology
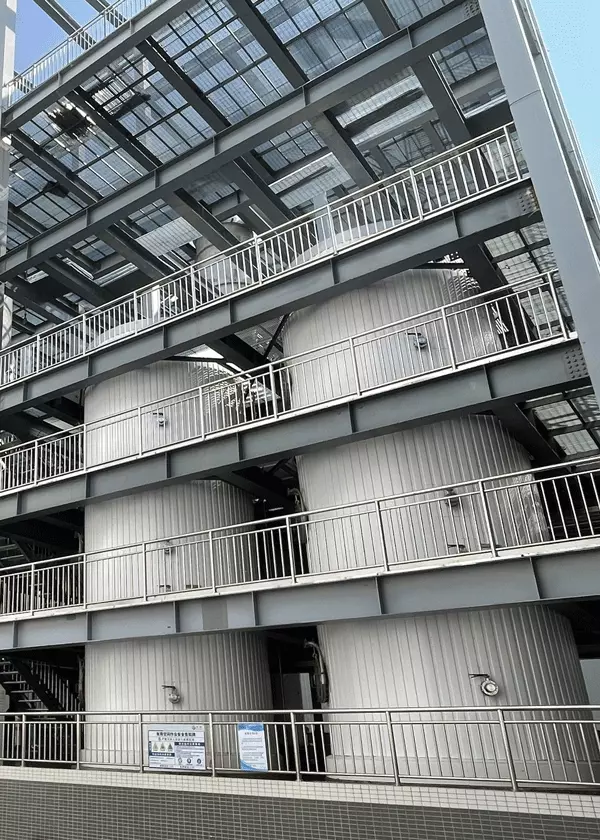

For lab analysis or pharma business, batch chromatography is commonly used whereas in food or biotech industries, cost and capacity constraints require systems with much higher productivity and much less eluent use, preferably water. That is why SMB (simulated moving bed), have been originally used, later on followed by SSMB (Sequential simulated moving beds) as most used reference
Therefore, chromatography became a technology of choice for large-scale purification processes of food product commodities :
High purity fractions.
No effluents or chemical consumption.
Very low operating cost, mostly electrical energy for water/eluent recycling.
Operating in continuous 24/7/365.
Resins, the fuel of the industrial
chromatography process
The liquid mixture is injected in columns containing the resin. The selection of the resin allows to separate the molecules from the mixture according to one or combination of 4 mechanisms:
- Ion exclusion (Ion exchange): molecules are separated based on their charges.
- Affinity: molecules are separated based on difference of specific interactions with the resin and the potential to form complex with the resin (ex Hydrogen bounds).
- Acid retardation: molecules are separated based on difference of ionization and solvation, in this case, the mobile phase is using a minor amount of acid.
- Size exclusion: molecules are separated based on size difference.
These mechanisms will affect the retention time of each molecules, allowing separation. Operating conditions (concentration, temperature, pH, …) and the properties of the resin influence the separation and are critical parameters to be studied in details.
Applexion Design & Build, Run & Perform and Upgrade & Revamp services are focusing in making the best understanding and best use of these interactions, from R&D to daily operation of an industrial system.
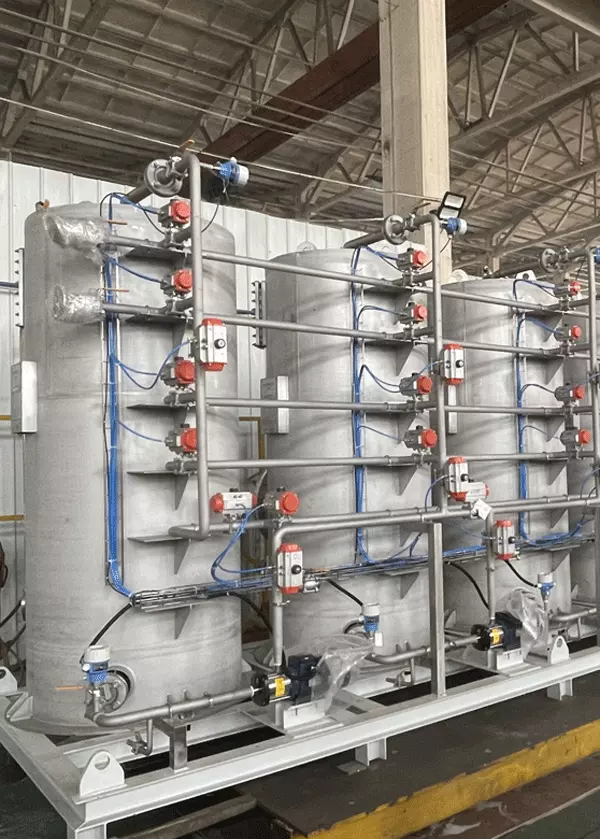


The System,
the engine of the industrial chromatography process
Now that we have the fuel (Resin & Operating conditions for a given product and target), let’s work on the engine to put that separation into the best motion.
Applexion™SC, more than a system, a methodology and wide range of possibilities.
Each separation requires a specific process design to get the best performances and Applexion™ SC meets this challenge by combining:
- A unique methodology to select THE solution tailored to your separation from a wide range of design options
- Applexion’s industrial expertise in building, commissioning and maintaining performance of chromatography systems
From R&D to plant start-up and beyond, Applexion™ SC offers a one-stop shop for all your chromatography projects: optimization of well-established applications as well as development of efficient purification processes for new products.
To find the best solution for your project and achieve maximum performance, Applexion works on a wide range of design alternatives to choose from: sequential [2 fractions (ex SSMB), 3 fractions ], cell design, resins, and flow distribution. Over the years, Applexion has developed or licensed the largest range of chromatography technologies for binary and tertiary separations
To go further on productivity and performance management, explore our wide range of services, upgrades & revamp possibilities.
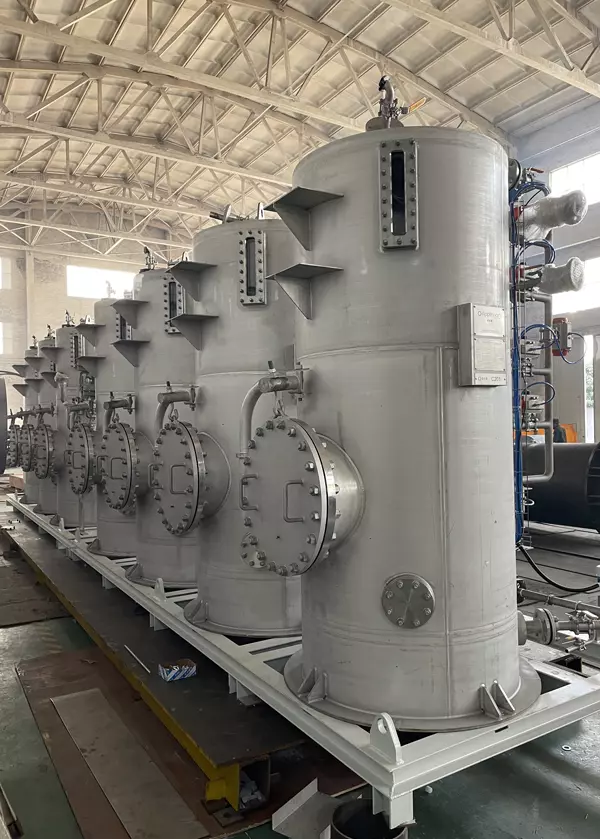


Let’s get more
technical
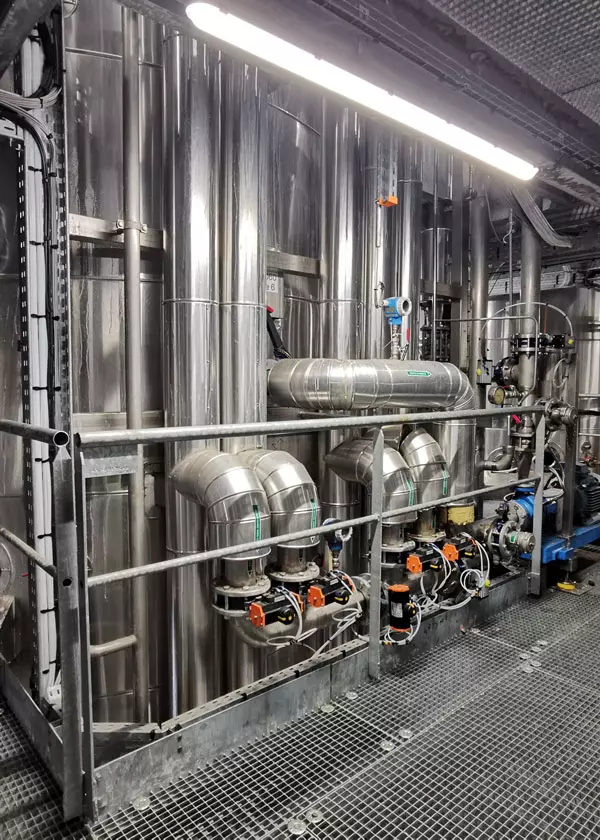
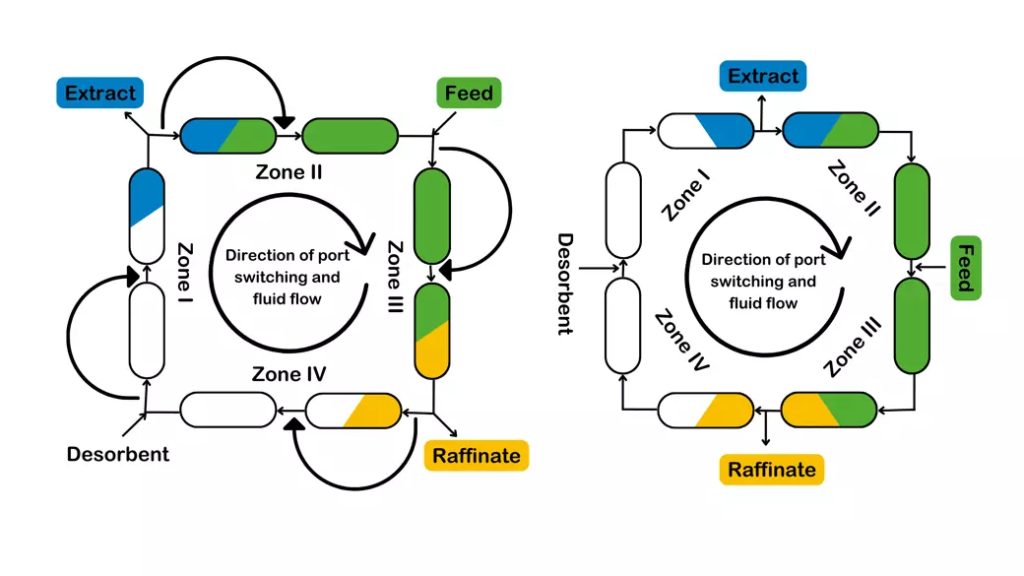
Binary separations: SSMB technology
Applexion™ Sequential Simulated Moving Bed (SSMB) in its current form is the latest generation and most advanced multi-column chromatography system for binary separation.
SSMB chromatography is the perfect technology to perform the continuous separation of two compounds or the binary fractionation of complex mixtures. It offers many advantages:
- Limited CAPEX and footprint (low number of columns)
- Reduced amount of installed resin
- High recovery and purity to up to 99%
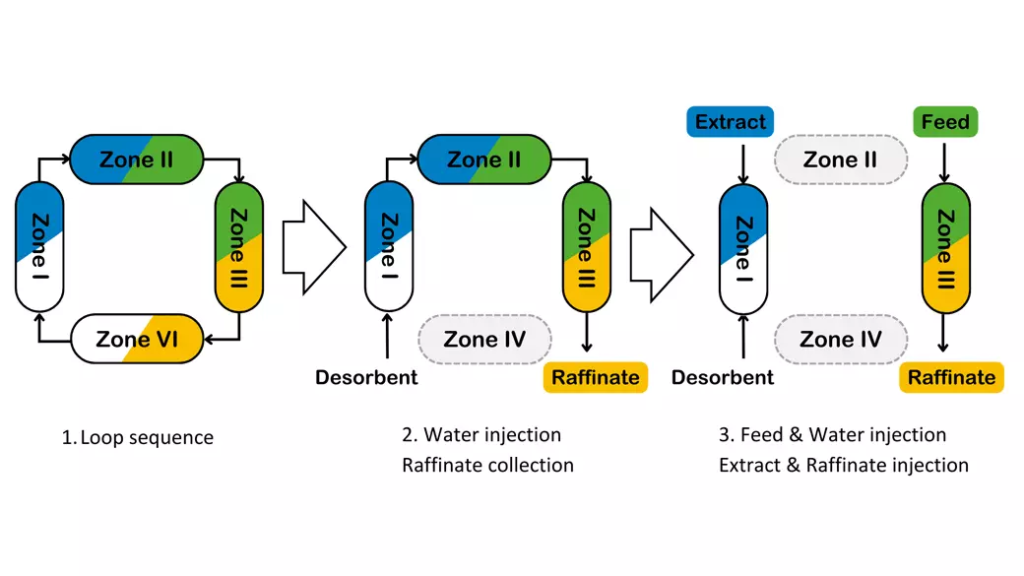
SSMB is a variation of the former SMB (Simulated Moving Bed) where a change of operation mode improve the performance. The conventional SMB is divided into three phases : feeding, circulation and elution.
SMB to SSMB sequential illustration
Tertiary separations
For these more complex separations, we aim deliver three fractions. Often, one fraction is the product of interest and the two others are valued through recycling at different stages within the complete process line. Dozens of three fractions processes have been published or promoted by different suppliers. In fact, these chromatography problems deserve often a tailor-made sequential to optimize the performances. The methodology is based on lab characterization, simulation, piloting and scaled up industrial design, and can be further used just like standardized two fraction processes.
Chromatography
Chromatography process design
By following our step by step approach, we manage to minimize scale up risks, shorten time to market for our industrial customers and maximize cost efficiency with our chromatography process design.
Our unique 3-step selection methodology ensures that you make the wisest choices among these alternatives and get the best design for your project:
- Resin screening test to find the best one for your process among Applexion™ XA resins, the industrial reference.
- Process simulation for quick and reliable exploration of numerous design alternatives.
- Pilot studies to validate the design and guarantee the industrial performance.
The very first point to start is the definition of the raw material to be purified. Which allow to define the final quality of the product and impurities to be removed. The quantity and the nature of these impurities will determine eventual pretreatments and the strategy of purification.

A screening of the chromatographic resins is performed at lab scale. Pre-selected resins are tested and compared regarding the performance of the separation. Resins are selected from our XA library, benefiting from our +50 years experience in industrial systems. Availability, regulatory aspects, quality, resistance to various stresses of the resins when going into industrial scale are key criteria of the selection.
One of the unique expertises of Applexion for a process development is digital modeling and process simulation. By combining experimental results of the current project, previous experience and our unique in-house software, we increase considerably the reliability of our results and hence the confidence in estimations that we can deliver from this stage of process development.
Numerical approach requires less raw material, smaller size of equipment and less time to explore a wider range of solutions. Moreover, it gives the capacity to test different constraints and to investigate in details the robustness of the design of the process. It is key for all new applications, where decades of feedbacks and learning are not available.

Here we build a design based on process simulation. A first mass balance is established with key values : size and design arrangement, flow rates ….and an estimation of the composition of the products obtained. It includes all consumptions such as process water, electricity, streams and related costs. This work, done together with process engineer and supported by technology experts will give a first evaluation of the CAPEX and OPEX of the system, benefiting from all Applexion experience in up-scaling from lab scale directly to industrial large system.
After this process evaluation based on lab screeining and process simulation, comes the next step for robust scale-up. Through pilot tests, key process settings corresponding to suitable performances can be confirmed or adjusted. Data for sizing can be confirmed and the robustness of the industrial process design proven. Piloting is not only process-oriented, but can be also product-oriented: the customer may need some kgs of product for market tests or further downstream trials.
The precise process design given with process performance guaranteed is the natural outcome of all the previous steps. At each step, an open dialogue with our customers allow a design customized to your specific needs and Applexion quality.
Chromatography
Some interesting facts
about chromatography
Often identified as available at a small scale and using high pressure and by consequence being an expensive technology. Applexion has been successfully providing its Sequential Chromatography technology to support a large panel of commodity products (food, fermentation, chemistry). Common applications involve purification of low value products such as Sugar molasses. Typical operating cost : 3 to 6$ / ton DS of Feed.
Since chromatography plays on unique parameters to accomplish the separation, it’s a fantastic ally for complementing existing purification technology. Great value is obtained using chromatography to recover product further from distillation bottoms or crystallization mother liquor.
Applexion team keeps innovating everyday.
- Multi-Fraction separation.
- in-silico separation simulation from bench scale.
- Various Fluid distribution technologies.
- Online monitoring and advanced controllers.
With chromatography technology, you don’t need to have someone monitoring the system all the time. Applexion Sequential Chromatography system is fully automated. It is generally based on various simulated moving bed technology and allows working 24 / 7 / 365.

Applications
Typical applications of the SSMB technology include the production of:
- HFCS 55/95/99, Crystalline fructose.
- High DX Glucose and crystalline dextrose.
- Polyols such as sorbitol, maltitol, mannitol, xylitol, etc.
- Commodity chemicals including MEG, PDO, glycine etc.
- Oligosaccharides (FOS, GOS, HMO, etc.).
- cellulosic sugars.
- Organic acids (citric acids, lactic acid,etc.).
- amino acids (tryptophane, phenylalanine, leucine, methionine, etc.).
- Recovery of valuable products in effluents and mother liquors.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the steps in chromatography?
In all chromatography the same steps are presents but can be named differently: feeding (injection of the product mixture) elution (separation of the products along the resin) and circulation phase (for continuous chromatography).
Is chromatography reliable?
Chromatography has been industrially used for decades now in different area such as food & feed industry, Pharma industry, functional ingredients industry, Biotech and chemical industry. Chromatography has been widely proven. Besides, methodology for development from lab to industrial scale has been improved and can be now supported by digitalization tools.
What is the basic use of chromatography?
In the food industry, historically, chromatography has been used for sugar separation. The separation of glucose and fructose after the isomerization step, to produce commodity sugars. Know the use can extended to all binary or tertiary separation respecting our table of separation technology.
Is Chromatography industrial system easy to use?
Yes, but it may need some training.
Industrial chromatography is set by a combination of 5 parameters (expressed generally in flowrate, volume or BV) which modifications plays on the balance of the separation within the system.
These modifications are required when facing a change. This change can be sudden (new target), or slow (resin fouling by ex).
Making the change and interpreting the need of a change require a strong expertise on the technology, the application and the system environment.
This is not easy.
Applexion has developped a set of digital services, Run & Perform, that provide automatic guidance on these matters.
So now, it is easy, safe & robust.
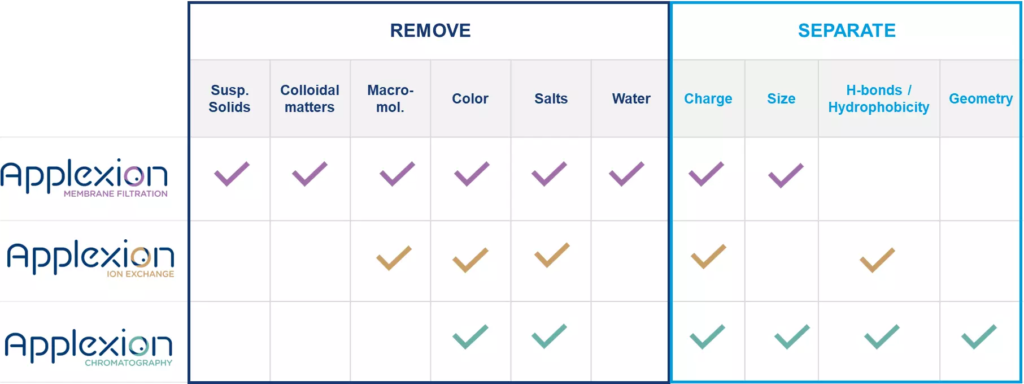
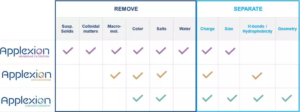
What is the difference between ion exchange, chromatography and filtration?
Type and strength of interaction of the product with a consumable (resin in this case) in given operating conditions.
From this differences and objective of the purification, we select the right technology to put in place.
Have a look to our separation table to understand the technology selection:

What are the advantages of chromatography?
Chromatography combine Technical efficiency and Green processing Technical efficiency because it is a precise separation with high recovery and high purity Green processing because of the absence of chemical reagent and minimized energetic consumptions.
What is the use of chromatography in industry?
Typical applications of the SSMB technology include the production of:
- HFCS 55/95/99.
- Crystalline fructose.
- Commodity chemicals including polyols (sorbitol, maltol, xylitol, etc.), MEG, etc.
- Oligosacharrides (FOS, GOS, IMO, etc.) and cellulosic sugars.
- Organic acids (citric acids, etc.).
- Aromatic amino acids (tryptophane, phenylalanine, etc.).
- Recovery of valuable products in effluents and mother liquors.
Why choose Applexion?
and offering on Chromatography, Ion exchange and Membrane filtration technologies.
The only global player, all over the world and all over the life cycle of your equipment.
You have a new one to share?
